General Relativity
Now let’s bring our understanding of relative to the general case where there could be a gravity well nearby (aka general relativity).
General Relativity is a theory of gravity that describes how gravity affects the curvature of spacetime. It builds on the principles of Special Relativity, following the natural consequences of the constancy of the speed of light further and leading to the emergence of gravity and the idea that space and time are not independent axes, but rather our reference frames are composed of a continuous spacetime.
Curved time creates gravity
Reframing our understanding of gravity
In Newtonian physics, gravity is a force that pulls objects together. On Earth, this would look like a uniform force acting on all objects pulling them towards the ground. But our exploration of Einstein’s postulate on inertial reference frames showed us that we can “flip” our reference frame and the physics are the same By this definition it is impossible to tell if you are at rest or in motion. So taking that to the extreme, maybe you are at rest and the Earth is accelerating upwards towards you!
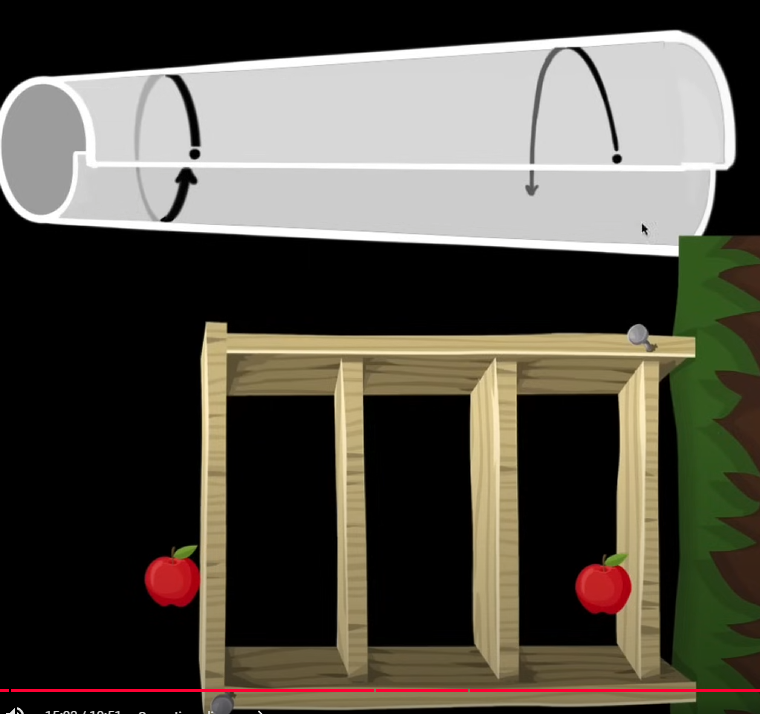
Now consider a photon. It travels in a straight line in space. In the reference frame where Earth is accelerating upwards, after a moment the photon is still traveling in a straight line but the ground is closer to it. More time passes and eventually the ground intersects the photon’s path. From the perspective of the Earth, it looks like the photon is bending towards the ground!
Video: Gravity bends light even though it has no mass
Now let’s get a laser and trace the path of its photons in the Earth’s reference frame. We observe that the photons are bent towards the ground, like before.
This time let’s measure the path of a photon at the top of the beam and at the bottom. To us, it appears that the photon at the top takes a longer path to reach the ground compared to the bottom photon. Our special relativity intuitions remind us that the speed of light is constant, so time must be slower for the top photon compared to the bottom photon. This is called gravitational time dilation.
I find this explanation profoundly unsatisfying. We can do better.
Geometric explanation
A more intuitive way to think about it is to think about it geometrically.
I don’t have the time or skills to make a beautiful animation for this, but the following video does an excellent job of explaining it:
Video: Gravity comes from time curving space
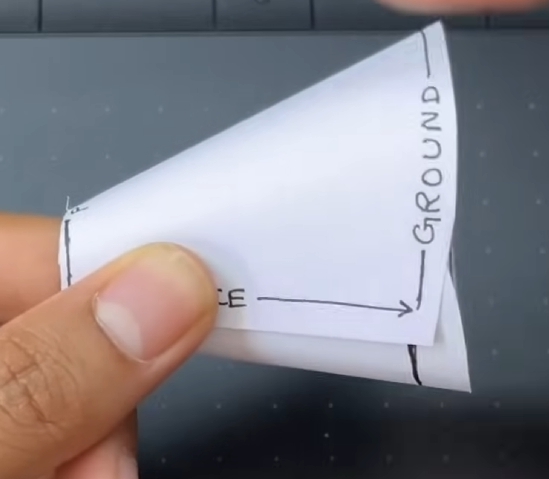

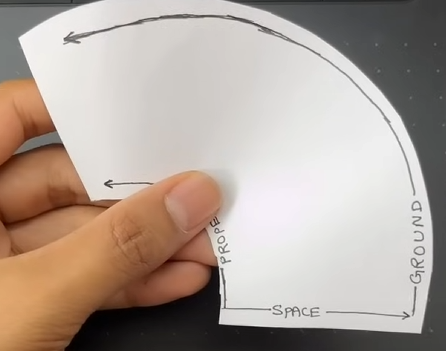
Curved spacetime
A key insight that will help us later is to understand that this definition holds true even if we morph the reference frame. So on the grid, an object would still move from point A to point B with respect to the reference frame. This is what we mean when we say that curved—all objects move along straight lines unless acted upon by a force, but the grid itself is getting morphed by gravity.
Video: Curved spacetime changes trajectories of light and matter